What Is The Surgical Removal Of One Or More Of The Parathyroid Glands?
Parathyroidectomy
Problems affecting theparathyroid glandscan cause an imbalance of calcium and crave removal of ane or more of the glands. Traditional parathyroidectomy involves a pocket-size incision in the front of the neck; however, newer transoral (through the oral cavity) procedures leave no visible scar and may be an pick.
What You Need to Know
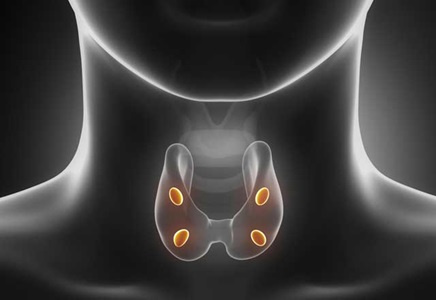
- The four parathyroid glands, each about the size of a grain of rice, are located behind the thyroid glandin the neck.
- Hormones from the parathyroid glands regulate blood levels of calcium and other minerals. Parathyroid gland problems requiring parathyroidectomy include hyperparathyroidism, parathyroid nodules and parathyroid tumors.
- Surgeons can access the parathyroid glands through an incision at the front of the neck, or through the mouth (scarless process).
Why might I demand a parathyroidectomy?
The parathyroid glands tin develop benign (or, rarely, malignant) growths that cause over- or under-product of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Radiations therapy, nutritional deficiencies and the use of some medications such equally lithium can likewise damage the parathyroid glands and affect their production of PTH.
An imbalance of PTH affects blood levels of calcium. Too piffling calcium can cause bone problems, depression, fatigue and other symptoms, while likewise much calcium can result in problems such as kidney stones, muscle spasms and nervus pain.
Claret tests, urinalysis, os density screenings and imaging tests tin can help the doctor determine if there is a problem with your parathyroid glands that requires removal.
What are the risks of parathyroidectomy?
-
Persistent low blood calcium levels
-
Vocalism changes, such as hoarseness
-
Sore pharynx
-
Bleeding and blood clots
-
Adhesions or scar tissue requiring further surgery
-
Injury to the esophagus or trachea (windpipe)
What happens during a parathyroidectomy?
Before the Procedure
The doctor may guild imaging and laboratory tests, such as:
-
Ultrasound, sestamibi nuclear medicine scan, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the parathyroid glands and surrounding areas
-
Blood test(s), urinalysis, bone density screening
-
Examination of the vocal cords and their function using an instrument called a laryngoscope
Just before your procedure, the surgical team may give you an antibiotic if you are prone to infections because of a problem with your immune system or other condition. You may receive medicines to reduce nausea and airsickness (antiemetics).
Unlike Types of Parathyroidectomy
Traditional Parathyroidectomy
About parathyroidectomies have identify while the person is under full general anesthesia, comatose and hurting-complimentary.
The surgeon makes a small incision in the peel of the neck and parts a thin layer of muscle to gain admission to the thyroid gland and the parathyroid glands behind it. The surgeon tin examine the parathyroid glands and remove those that are damaged or affected by disease.
The surgeon then returns the muscles of the front of the neck to their proper position and secures them in place. The skin is airtight with sutures or glue.
Cervix Surgery'southward Scarless Alternative
When Gwen met with caput and neck endocrine surgeon Jonathon Russell, M.D. , at Johns Hopkins to discuss a thyroidectomy, she mentioned symptoms such as low os density, fatigue and kidney stones. Russell diagnosed Gwen with hyperparathyroidism acquired by a parathyroid nodule.
Scarless (Transoral) Parathyroidectomy
This is a newer technique for select patients that involves accessing the parathyroid glands through the oral fissure. This surgery leaves no visible scar since there is no incision on the outside of the neck.
Parathyroidectomy: Recovery and Next Steps
After a parathyroidectomy, you are probable to go dwelling house with some calcium supplements until the remaining normal parathyroid glands "wake up" and resume functioning.
Source: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/parathyroidectomy
Posted by: feasterthereappos.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Surgical Removal Of One Or More Of The Parathyroid Glands?"
Post a Comment